Research Impact
Impact is change – what has changed because of what you did?
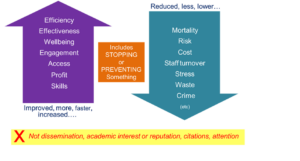
Long description: A diagram that highlights what can be improved by impact or alternatively reduced by impact, improved includes; Efficiency, Effectiveness, Wellbeing, Engagement, Access, Profit and Skills. Reduced includes; Morality, Risk, Cost, Staff turnover, Stress, Waste and Crime.
Improved, more, faster, increased:
- Efficiency
- Effectiveness
- Wellbeing
- Engagement
- Access
- Profit
- Skills
Includes: stopping or preventing something
Reduced, less, lower:
- Mortality
- Risk
- Cost
- Staff turnover
- Stress
- Waste
- Crime
- Etc…
Not dissemination, academic interest or reputation citations, attention.
Research Impact is:
An effect on, change or benefit to the economy, society, culture, public policy or services, health, the environment or quality of life.
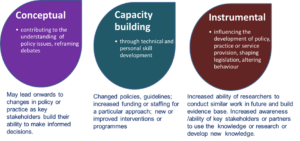
Impact includes an effect, change or benefit on:
- Processes: the activity, attitude, awareness, behaviour, capacity, policy, opportunity, performance, practice, or understanding;
- People: an audience, families, beneficiary, community, constituency, or individuals;
- Places: any organisation or geographic location whether locally, regionally, nationally or internationally
What is research impact: REF2021 Definition
- “assess the ‘reach and significance’ of impacts on the economy, society, culture, public policy or services, health, the environment or quality of life that were underpinned by excellent research conducted in the submitted unit.”
- “the impact would not have occurred or been significantly reduced without the contribution of the research.”
What is research impact: Academic Impact
“The demonstrable contribution that excellent research makes to academic advances, across and within disciplines, including significant advances in understanding, methods, theory and application.” RCUK
Online resources/Tool kit
- ESRC Impact Toolkit
- Fast Track Impact
- Impact Literacy Workbook
- Becker Medical Library (Biological Sciences)